 6Reptiles on Land
6Reptiles on Land
Around 310 million years ago the first reptiles started getting comfortable with life up on dry land. On earth today, the reptiles family includes snakes, lizards, crocodiles, turtles, and tortoises. There are currently about 10,700 different species of reptiles with only around 100 that are classified as marine reptiles.
Evolution: From Fish to Reptiles
Reptiles are descendents of fish. We have abundant fossils of ancient fish, and of ancient reptiles. For many years scientists searched for fossils of an animal that was the “missing link” that showed what animals were like in the era during the transition to life on land. The discovery of the Tiktaalik fossil helped scientists put together a more complete picture of how fish evolved into reptiles. Tiktaalik appeared about 375 million years ago and was the link between swimming fish and land-based reptiles. Tiktaalik had a strong backbone, plus a newly evolved neck that enabled it to lift its head.
These transitional creatures had strong flippers so it could lift itself up (like doing pushups!) and climb out of the water and onto land. These flippers evolved into four limbs that were the forerunners of arms and legs.
But once creatures like Tiktaalik could lift their heads, they could see food on land such as insects, and were motivated to venture out of the water. The land was an unexplored ecosystem with many opportunities.
Reptiles: Four Limbs

Fish have fins, while land-living animals have limbs with fingers, toes, wrists and ankles.
Examining a fin, we see bones that correspond to the upper arm, the forearm and even parts of the wrist.
Tiktaalik: An Amphibian
Tiktaalik didn’t evolve directly into a reptile. First, it became an amphibian.
Amphibians appeared about 365 million years ago, and reptiles evolved from their amphibian ancestors at least 300 million years ago.
Reptiles: Ancestor of All Creatures with Limbs
Today, all animals with limbs that live on land (including humans) are descended from reptiles.
Reptiles: Physical Traits

The protective scales that cover reptile bodies later evolved into the hair, fur and feathers of mammals, including humans, and birds.
Reptile claws evolved into human fingernails and toenails.
Reptiles: Blood
Reptiles are cold-blooded, meaning their internal temperatures depend on the temperature outside. Their hearts have three chambers.
Reptiles: Egg Laying
Most reptiles lay eggs with soft, leathery shells, and most do not provide any kind of care to their offspring. Reptile babies, such as turtles, must fend for themselves from the time they are hatched.
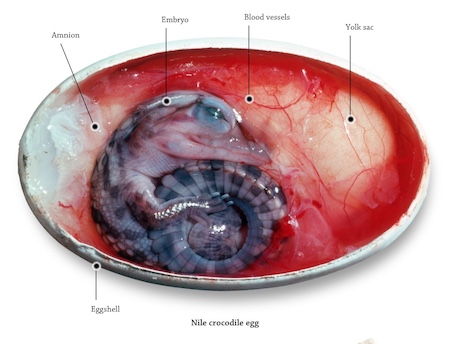
Over time, one branch of the reptile family evolved a new way of raising babies.
What do You have in Common with Reptiles?
Your body is adapted to live on dry land. You have lungs that can breathe oxygen. You have four limbs.
What's Next?
A branch of the reptile family split off and evolved into a mammal.
Learn More:
Hair, scales and feathers descend from single reptilian ancestor
This article looks at “reptiliomorphs” which likely carried features of reptiles and amphibians and are the common ancestor of birds, mammals and reptiles.
Amphibians were common ancestors of reptiles and mammals
https://www.amnh.org/exhibitions/permanent/reptiles-amphibians
Amphibians were the first vertebrates to live on land and are the group from which mammals and reptiles, including birds, evolved.
Seven traits humans got from reptiles
http://mentalfloss.com/article/55873/7-traits-humans-inherited-reptiles
Human and reptilian brains share many traits
https://massivesci.com/articles/lizard-people-reptile-brain-human/
Human and lizard brains are similar
https://www.amnh.org/exhibitions/brain-the-inside-story/your-emotional-brain/beyond-our-lizard-brain
