 2Complex Cells
2Complex Cells
Around 2.7 billion years ago, a branch of LUCA’s family evolved into complex cells. This evolutionary step led to all the animals and plants in the world today. At first, all complex cells were unicellular creatures.
Evolution: The Transition from Simple Cells (like LUCA) to Complex Cells
For over a billion years all life on earth was made from simple, prokaryotic cells.
One of the biggest turning points in the history of life happened when a new type of complex cell emerged.
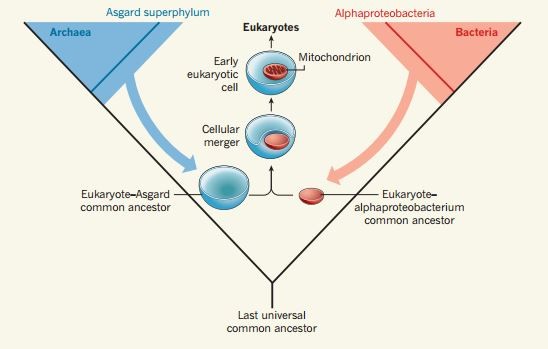
Scientists think this most likely began when one large cell swallowed a smaller one, and the two were able to work together as a new kind of single cell. When these two different types of cells merged and evolved a way of working together as one cell they created a new, complex - eukaryotic - cell structure.
Their advantages over single-celled organisms included added chemical energy which made the cells more robust and extra protection given to the cell’s inner workings.
All animals, plants and fungi are made from eukaryotic cells.
Organelles
These new complex cells also have specialized features called organelles. Each cell has many different types of these small organs, and each performs a unique function.
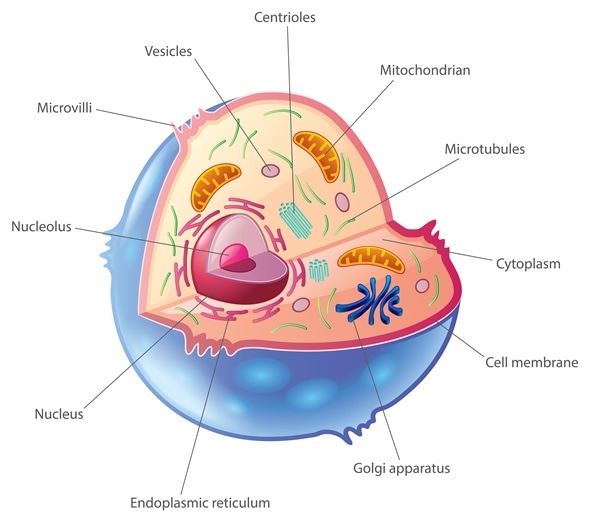
The largest and most important organelle is the nucleus.
Sexual Reproduction
For eukaryotes, sexual reproduction emerged about 1.2 billion years ago.
In asexual reproduction, offspring are identical to the parent. If the environment changes, these offspring may not fit in, and the species may eventually go extinct.
Because sexual reproduction creates offspring that are slightly different, some will be more likely to survive in the changed environment. Sexual reproduction creates greater genetic diversity. Because of sexual reproduction the pace of evolution started to speed up. More variety leads to a greater rate of change.
Over time, the Eukaryotic family split into three branches: Plants, fungi and animals.
Plants Emerge
About 2 billion years after Eukaryotic cells first appeared, the earliest plants emerged in the ocean in the form of green algae.
Modern-day plants evolved from these aquatic algae, which did not have stems or roots.
Animals Emerge
When did the animal split off? Because this occurred so long ago and left virtually no fossil evidence, scientists disagree about when animals first appeared. Most estimates are roughly 570 million years ago, although the figure is also estimated to be as long ago as 650 million years.
As more groups of complex cells began working together, a branch of the family split off and evolved into multicellular animals.
What do You have in common with a Single Celled Eukaryote?
All the cells in your body (your face, heart, bones, everything) are eukaryotic cells made with this same complex cell structure.
What's Next?
The Transition from Single-Celled Eukaryotes to Multicellular Animals.
A branch of the single-celled Eukaryote family split off and evolved into the first multicellular organisms.
Learn More:
How giant viruses helped Eukaryotes evolve from prokaryotes
https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2018/02/180207102751.htm
Eukaryotic lineage appears about as ancient as the two prokaryotic lineages.
https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/when-did-eukaryotic-cells/
Amoeba Sisters: Good side-by-side comparison of prokaryotes & eukaryotes (5:27)
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Pxujitlv8wc
Good comparison of prokaryotes & eukaryotes (4:42)
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zZtcMBTQaS4
